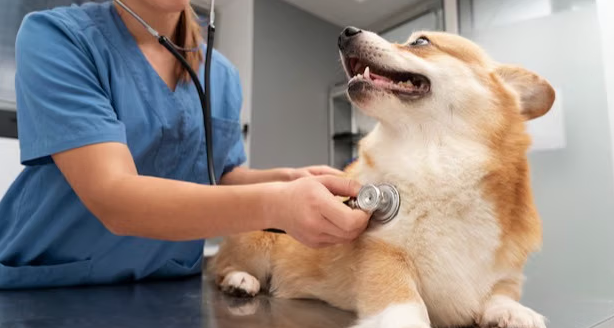
What is the process of sterilization a dog?
Process Of Dog Sterilization Before And After: Know About It: The Supreme Court has said in its order of 22 August that now only aggressive and rabies-infected dogs will be kept in shelter homes. While all the other stray dogs have been instructed to be returned to their current place after sterilization and vaccination. To know the entire process from the sterilization of dogs to their operation and release back.
What Is Dog Sterilization Or neutering?
Dog neutering is a medical procedure in which a male dog’s testicles are surgically removed to prevent reproduction. It is carried out by a qualified veterinarian under anesthesia, ensuring the dog feels no pain during the operation. Neutering not only stops the dog from fathering puppies but also helps reduce hormone-driven behaviors such as aggression, excessive roaming, and territorial marking. It is a common and safe procedure that contributes to better behavior and overall population control of stray dogs.
1. Catching and Bringing Dogs to the Camp or Clinic
Stray dogs are first caught from their respective areas and brought to a designated sterilization center or camp. This is usually done by trained animal handlers or municipal teams using safe and humane methods.
2. Pre-Surgery Fasting and Medication
Before the surgery, dogs are kept fasted for at least 12 hours. This is to ensure they don’t vomit under anesthesia, which could lead to complications. During this period, dogs are also given antibiotics and pain-relief medication to prevent infection and manage pain after surgery.
3. Anesthesia Administration
Dogs are given anesthesia shortly before surgery to ensure they don’t feel pain and remain calm during the procedure. The effect of the anesthesia lasts for around 30 minutes, during which the surgery must be completed.
4. Surgical Setup and Team Involvement
The sterilization center has an operating theatre with oxygen support. Each surgery team typically includes a surgeon (veterinary doctor), an assistant veterinarian, and two support staff. All surgical tools like scalpels, forceps, and needles are sterilized in advance to maintain hygiene and prevent infection.
5. Number of Dogs Sterilized at a Time
The number of dogs sterilized at once depends on the capacity of the camp. Typically, 5 to 10 dogs can be prepared at one time, depending on the availability of beds, staff, and resources.
6. Surgical Procedure (During the Operation)
The operation takes 30 to 45 minutes. In male dogs, the testes are removed. In female dogs, both the uterus and ovaries are removed. This completely stops their ability to reproduce and helps in controlling the stray dog population.
7. Difference Between Human and Dog Sterilization
In dogs, actual reproductive organs are removed during sterilization. In contrast, human sterilization usually involves tying or cutting reproductive tubes (vas deferens in males, fallopian tubes in females), not removing organs. This makes dog sterilization more invasive.
8. Post-Operation Recovery
After surgery, dogs are shifted to a recovery ward within 20–25 minutes. They are kept under observation. A liquid diet is introduced after 4–5 hours. Male dogs are kept for 3 days, while female dogs require 5 days of post-operative care due to the more invasive nature of their surgery.
9. Release Back to Original Location
Once they recover, dogs are returned to the same location from where they were picked up. This is in line with the Supreme Court’s directive, which states that only aggressive or rabies-infected dogs should be kept in shelters.
10. Recovery and Return to Normal Behavior
Dogs begin to return to normal behavior within 24 hours, though full recovery may take 1–2 days. During this time, they are given light food and clean water, and are monitored for any complications.
ALSO READ: Nayanthara Upcoming Movies